Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a viral pathogen that plays a crucial role in respiratory illnesses, especially among infants, young children, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immune systems. Understanding the causes, available treatments, and prevention strategies for hMPV is essential in reducing its impact and managing the associated health risks.
What is Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV)?
Human metapneumovirus is a member of the Paramyxoviridae family and closely related to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). It was first identified in 2001 and has since been recognized as one of the key causes of respiratory infections worldwide. hMPV infects both the upper and lower respiratory tracts, contributing to symptoms that range from mild to severe, sometimes leading to hospitalization.
Causes of Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Infection
hMPV is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or even talks. It can also be transmitted by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes. The virus is highly contagious, especially during peak respiratory virus seasons in the fall and winter months.
While anyone can contract hMPV, certain groups are at higher risk of developing severe symptoms:
- Infants and young children: Due to their immature immune systems, they are particularly vulnerable to respiratory distress.
- Elderly adults: Aging can weaken the immune system, making older adults more susceptible to severe infections.
- Individuals with underlying conditions: People with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or immunosuppressive treatments may experience worsened symptoms.
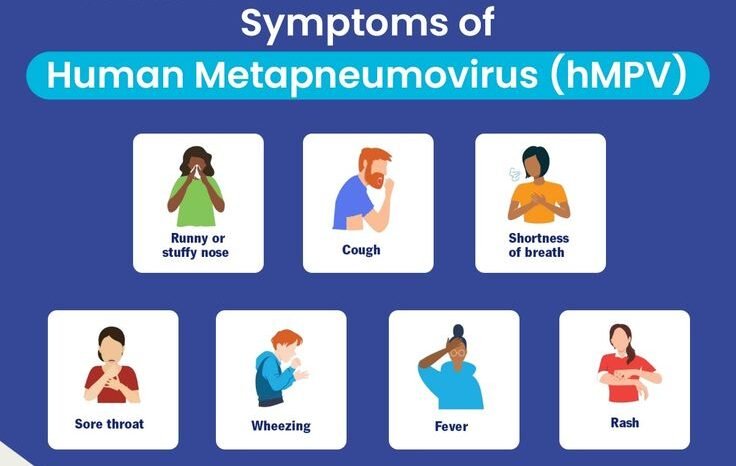
Symptoms of hMPV Infection
The symptoms of an hMPV infection often mimic those of other viral respiratory infections. These may include:
- Mild symptoms: Runny nose, cough, sore throat, mild fever, fatigue.
- Severe symptoms: Difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. In more extreme cases, hMPV can lead to bronchiolitis or pneumonia, requiring medical intervention.
In young children and vulnerable adults, hMPV can cause significant respiratory distress and may require hospitalization, especially if the individual has underlying health conditions.
Treatment of Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV)
Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication to treat hMPV infections. Management typically involves supportive care, which aims to relieve symptoms and help the body recover from the infection. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and hydration: To support the immune system.
- Fever reduction: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce fever and alleviate discomfort.
- Oxygen therapy: In severe cases, especially in hospitalized patients, oxygen may be administered to aid breathing.
- Mechanical ventilation: For critically ill patients with severe respiratory distress, mechanical ventilation may be required.
In most cases, individuals recover from hMPV infections within one to two weeks, although young children, elderly adults, and those with weakened immune systems may take longer to recover and may experience more serious complications.
Prevention Strategies for hMPV
As there is no vaccine currently available for hMPV, prevention focuses on limiting its spread and reducing the risk of infection. Here are key strategies to prevent the transmission of hMPV:
- Frequent handwashing: Washing hands regularly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of respiratory viruses.
- Avoid close contact: Try to limit close contact with individuals who show symptoms of a respiratory illness, especially during the viral season.
- Cleaning surfaces: Disinfect frequently touched surfaces such as doorknobs, phones, keyboards, and remote controls to prevent the spread of germs.
- Covering coughs and sneezes: Always cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of droplets.
- Avoiding crowded places: Staying away from crowded areas, especially during flu season, can reduce the risk of exposure to respiratory viruses.
- Boosting the immune system: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can strengthen the immune system and help prevent infections.
Conclusion
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a significant respiratory pathogen that can affect people of all ages, particularly those with weakened immune systems. While there is no specific antiviral treatment, supportive care can help manage the infection and reduce symptoms. Prevention strategies, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, are essential in reducing the spread of hMPV. As research continues, it is hoped that vaccines and more effective treatments will become available to better control the impact of hMPV on public health.

